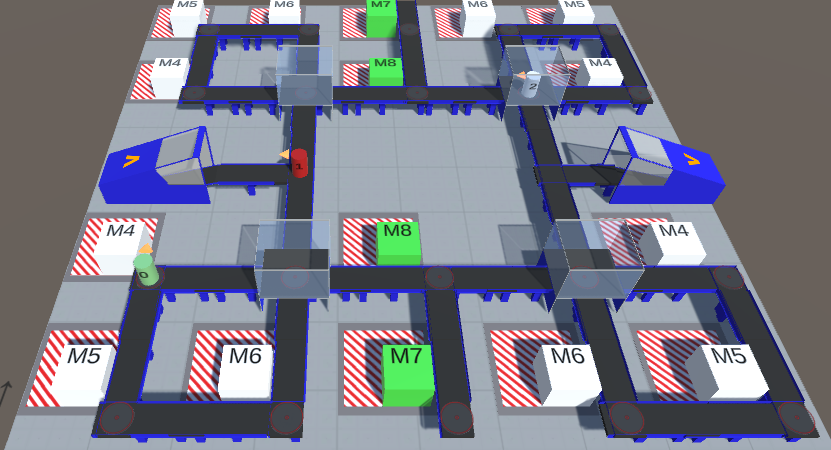
We focus on resilience in cooperative multi-agent systems, where agents can change their behavior due to udpates or failures of hardware and software components. Current state-of-the-art approaches to cooperative multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL) have either focused on idealized settings without any changes or on very specialized scenarios, where the number of changing agents is fixed, e.g., in extreme cases with only one productive agent. Therefore, we propose Resilient Adversarial value Decomposition with Antagonist-Ratios (RADAR). RADAR offers a value decomposition scheme to train competing teams of varying size for improved resilience against arbitrary agent changes. We evaluate RADAR in two cooperative multi-agent domains and show that RADAR achieves better worst case performance w.r.t. arbitrary agent changes than state-of-the-art MARL.
@article{ phanAAAI21,
author = "Thomy Phan and Lenz Belzner and Thomas Gabor and Andreas Sedlmeier and Fabian Ritz and Claudia Linnhoff-Popien",
title = "Resilient Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning with Adversarial Value Decomposition",
year = "2021",
abstract = "We focus on resilience in cooperative multi-agent systems, where agents can change their behavior due to udpates or failures of hardware and software components. Current state-of-the-art approaches to cooperative multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL) have either focused on idealized settings without any changes or on very specialized scenarios, where the number of changing agents is fixed, e.g., in extreme cases with only one productive agent. Therefore, we propose Resilient Adversarial value Decomposition with Antagonist-Ratios (RADAR). RADAR offers a value decomposition scheme to train competing teams of varying size for improved resilience against arbitrary agent changes. We evaluate RADAR in two cooperative multi-agent domains and show that RADAR achieves better worst case performance w.r.t. arbitrary agent changes than state-of-the-art MARL.",
url = "https://ojs.aaai.org/index.php/AAAI/article/view/17348",
eprint = "https://thomyphan.github.io/files/2021-aaai.pdf",
journal = "Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence",
pages = "11308--11316",
doi = "https://doi.org/10.1609/aaai.v35i13.17348"
}
Related Articles
- T. Phan et al., “Adaptive Anytime Multi-Agent Path Finding using Bandit-Based Large Neighborhood Search”, AAAI 2024
- T. Phan et al., “VAST: Value Function Factorization with Variable Agent Sub-Teams”, NeurIPS 2021
- T. Phan et al., “Learning and Testing Resilience in Cooperative Multi-Agent Systems”, AAMAS 2020
- T. Gabor et al., “The Scenario Coevolution Paradigm: Adaptive Quality Assurance for Adaptive Systems”, STTT 2020
- T. Gabor et al., “Scenario Co-Evolution for Reinforcement Learning on a Grid World Smart Factory Domain”, GECCO 2019
- T. Phan, “Emergence and Resilience in Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning”, PhD Thesis
Relevant Research Areas